The Mediterranean is the largest sea that cannot yet be called an ocean. Bordered to the north by Western Europe, to the south by Africa and to the east by the Middle East, this sea is surrounded by many of the world’s oldest civilizations.
Seas and oceans play a fundamental role in the evolution and variability of the climate, due to their interaction with the atmosphere and because they absorb approximately 25% of the CO2 emitted annually into the atmosphere as a result of human activities, according to data from the
Meteorological Service of Catalonia.
. In this framework, knowledge of the past evolution and future trends of sea surface temperature is crucial for future climate scenarios.
Sea temperatures can be used to detect and predict the development and/or intensification of heavy precipitation in the Mediterranean basin and even in other areas of the world. Its importance has also been demonstrated in the study of heat waves in Europe. Therefore, being attentive to the temperature of the sea and its evolution is an important ingredient if you want to enjoy it.
There is a good degree of temperature variation in the waters of the Mediterranean. It is generally much warmer as one travels eastward and there is a range of about 10°C between winter and summer highs and lows.
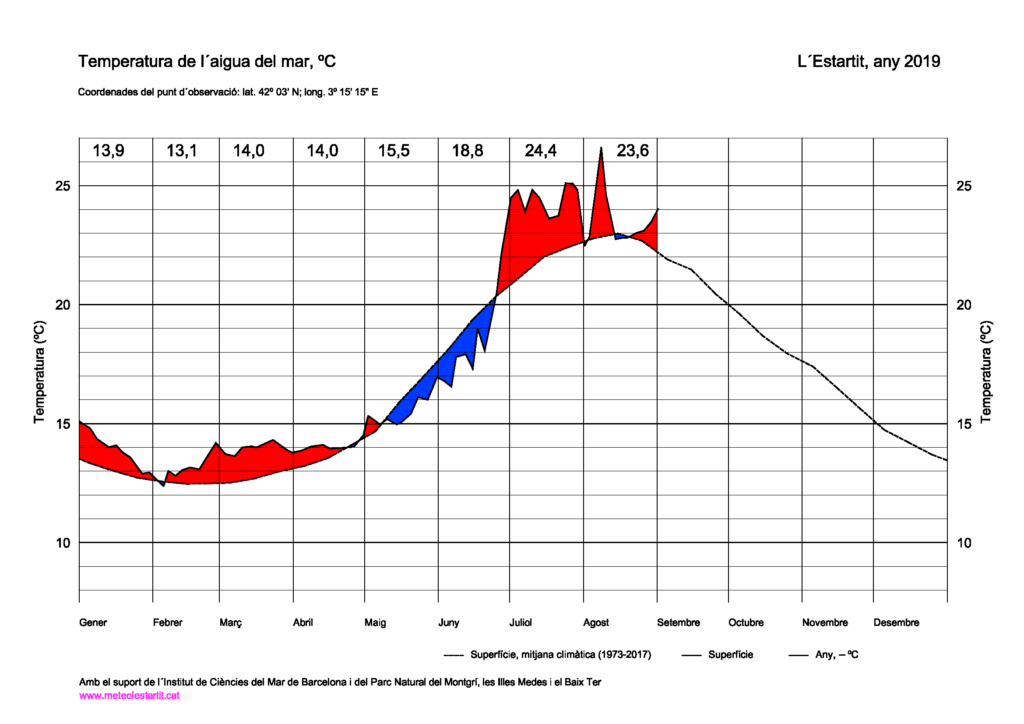
If we want to be more precise, we are fortunate in Catalonia to have a series of maritime data for more than forty years and regularly taken 2 miles offshore from the port of Estartit, just over a mile from the Medes Islands (42° 03′ LATO N / 3° 15′ 15′ 15” LONG E).
At this 90-meter depth point, temperature measurements are taken from 1969 at seven depth levels (surface, -20, -50, -80 meters).
According to data from the
Estació Meteorològica de l’Estartit i de Torroella de Montgrí
Since 1974, the annual median seawater temperature has increased significantly at all levels. At the surface it does so at a rate of +0.32 °C/decade, at 20 m depth it is +0.30 °C/decade, at 50 m it does so at a rate of +0.26 °C/decade and at 80 m at +0.20 °C/decade.
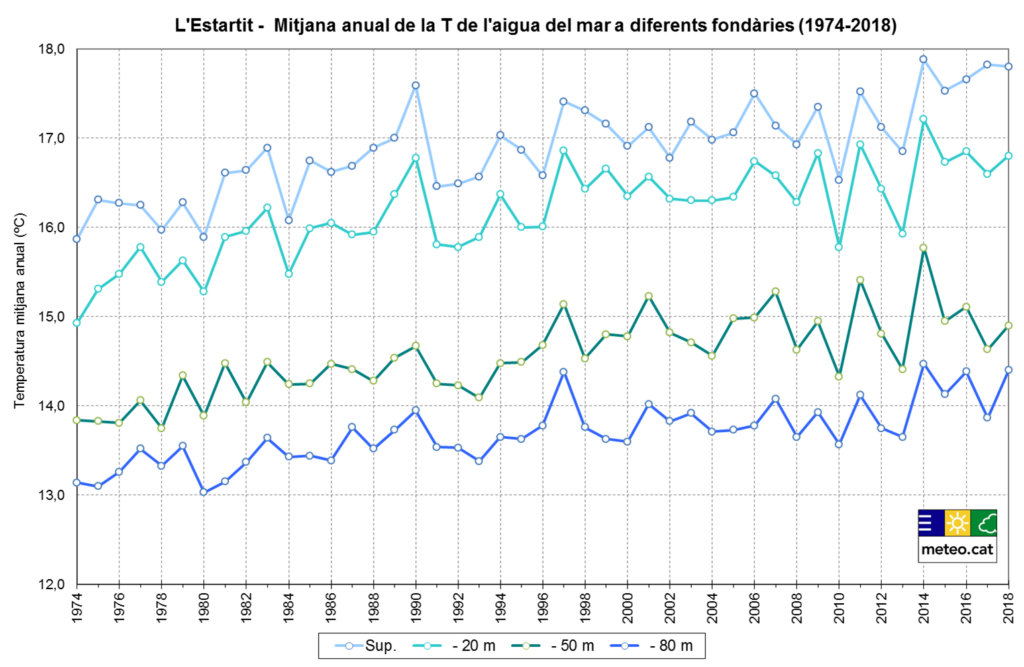
The year 2018 had a positive anomaly of +0.9 °C at the surface, the third highest in the entire series.
Broadly speaking, we can say that seasonally, autumn and summer are the times of the year with the most evident warming trend, especially at 20 m and 50 m depth, with values exceeding +0.30 °C/decade.
The Institute of Statistics also offers a panoramic view of the evolution of our Mediterranean Sea.
